Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undergone an explosive evolution in recent years. According to McKinsey’s 2024 report, over 60% of organizations globally have adopted at least one AI technology, and generative AI tools have seen adoption rates grow by more than 300% year-over-year. This surge of interest has paved the way for a new paradigm: agentic AI. Rather than waiting for user prompts, agentic AI can plan, make decisions, and execute tasks on behalf of users.
This blog will provide a comprehensive understanding of generative AI vs agentic AI, how they differ, and where they are most useful. We’ll explore their core features and why the growing shift toward agentic AI is reshaping the future of intelligent systems.
What are generative AI vs agentic AI?
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to AI systems designed to generate new content based on input data. This includes text, images, videos, audio, and even code. It relies heavily on advanced machine learning models such as:
- Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for image synthesis
- Diffusion Models for high-resolution visuals (used in tools like Midjourney and Stable Diffusion)
These models are trained on vast datasets and learn to mimic human-like patterns. Tools like ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, and DALL·E are popular examples of generative AI in action.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI, on the other hand, refers to systems that are capable of acting autonomously to achieve a specific goal. Instead of merely generating content, agentic AI is designed to plan, reason, use external tools or APIs and adapt to changing conditions.
Agentic AI typically includes components such as:
- A language model (GPT-4)
- A planner or goal interpreter
- Memory systems to retain context across actions
- Tool integration (browsers, APIs, code execution)
Well-known examples include:
- AutoGPT: An experimental system that loops through reasoning and execution steps
- Devin: An AI software engineer that builds and debugs code end-to-end
- LangChain agents: Frameworks for creating custom task-performing agents
Agentic AI vs AI Agent
While often used interchangeably, agentic AI and AI agent refer to different layers of the same concept. All AI agents follow agentic AI principles, but they differ in complexity, purpose, and how broadly they can operate.
- Agentic AI is the overarching paraagen, AI systems capable of planning, reasoning, and acting autonomously.
- AI agents are implementations of that paradigm, built with specific tools (like AutoGPT or LangChain) to perform defined tasks.
Features of generative AI vs agentic AI
Generative AI features
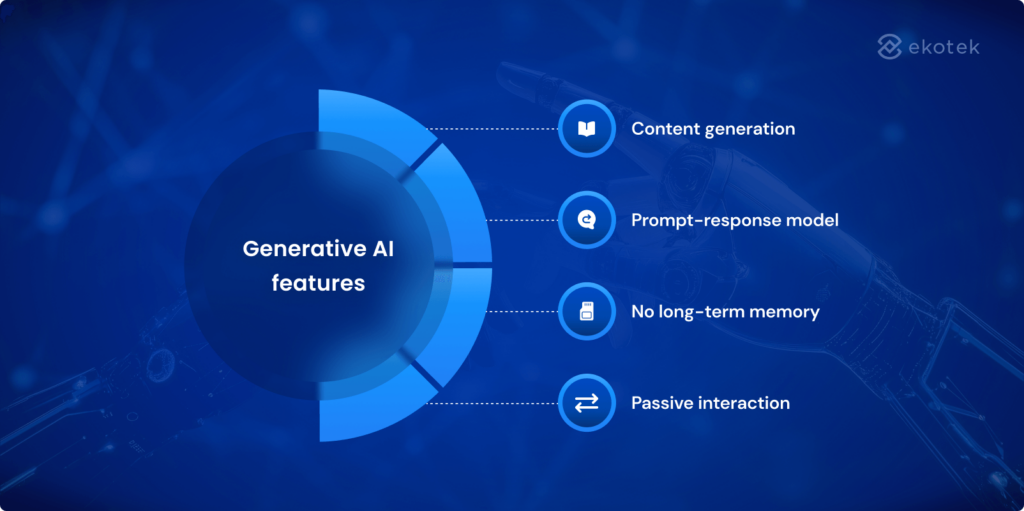
- Content generation: Generative AI can create original content such as text, images, audio, video, or code. It is widely used in writing, design, programming, and creative arts.
- Prompt-response model: Gen AI operates on a “prompt and response” model. The user provides an input (prompt), and the AI responds with relevant output. It does not take further action unless explicitly instructed.
- No long-term memory: Most generative AI models do not retain memory across sessions. Each interaction is treated independently from the last. Some systems, however, can be enhanced with long-term memory features if needed.
- Passive interaction: Generative AI waits for user input before doing anything. It does not initiate tasks or make proactive decisions. This makes it ideal for controlled, on-demand use cases.
Agentic AI features

- Task planning and completion: Agentic AI can plan and carry out complex, multi-step tasks like researching, summarizing, and emailing. It handles goals systematically instead of just responding to single commands. This enables it to complete workflows from start to finish.
- Tool use: Agentic AI is capable of using external tools such as APIs, browsers, or file systems. It goes beyond content generation to interact with digital environments. This flexibility makes it more powerful than basic generative systems.
- Memory and learning: Unlike Generative AI, Agentic AI can remember previous interactions and learn from outcomes. It uses this memory to improve performance and adapt to user preferences. Over time, it becomes more efficient and personalized.
- Autonomy: Agentic AI can make decisions and act independently with minimal human input. It identifies opportunities, evaluates situations, and takes initiative. This level of autonomy is what defines it as a true “intelligent agent.”
Key differences between Generative AI vs Agentic AI
| Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Core purpose | Content creation | Goal-driven execution |
| Interaction style | Prompt-based | Goal-oriented and autonomous |
| Memory | Stateless (no memory between sessions) | Often stateful with memory and context retention |
| Autonomy | Low, requires constant user input | High, can act with minimal supervision |
| Output type | Single-step results | Multi-step process and task chaining |
| Decision making | No decision-making capabilities | Can make decisions based on conditions and goals |
| Context awareness | Limited to current prompt | Maintains and uses broader context across actions |
| Tool integration | Limited, usually doesn’t use external tools | Can use APIs, browsers, files, databases |
| Adaptability | Static, behaves the same unless re-prompted | Dynamic, learns and adjusts strategies during task execution |
| Use cases | Creative writing, design, content generation | Automation, personal assistants, research agents, task handlers |
| Initiative | None, reacts only to direct prompts | Can initiate tasks or follow-up steps proactively |
| Workflow involvement | Isolated use, one-off outputs | End-to-end workflow, handles full task pipelines |
| Evaluation | User-driven evaluation of outputs | Self-evaluates or re-tries based on goal success/failure |
As we’ve seen, the differences between generative AI and agentic AI go far beyond just content generation versus automation. While Generative AI is powerful in producing creative outputs from prompts, Agentic AI is designed to execute complex, goal-driven workflows with autonomy and memory. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each helps businesses and developers choose the right type of AI for their specific needs.
Use cases for Generative AI vs Agentic AI
Generative AI use cases

- Marketing content creation: Generative AI can write blogs, social media posts, product descriptions, and ad copy quickly. This saves marketers time and ensures a consistent brand voice. It’s especially useful for content teams with high-volume needs.
- Image and art generation: Tools like Midjourney and DALL-E use Generative AI to create original visuals for campaigns. Designers can explore multiple creative directions without starting from scratch. This accelerates design workflows and boosts creativity.
- Code suggestions: Generative AI helps developers by generating code snippets, suggesting improvements, or even fixing bugs. It reduces development time and supports beginners. Platforms like GitHub Copilot are prime examples.
- Education and tutoring: AI-powered tutors can generate quizzes, explanations, and personalized lesson plans. Students get instant help tailored to their level. This makes education more accessible and scalable.
- Language translation and localization: Gen AI can translate text and localize content across multiple languages while preserving tone and context. This helps businesses scale globally and connect with diverse audiences. It’s especially valuable for international marketing, support, and education.
⭐️ Download our e-book – Generative AI use cases for enterprises
Agentic AI use cases

- Workflow automation: Agentic AI can execute multi-step tasks like lead scoring, sending follow-up emails, or onboarding clients. It connects multiple tools and performs actions in sequence. This frees up time for human workers to focus on higher-value work.
- AI software developers: Agentic systems like Devin can plan, write, test, and debug software autonomously. They act like virtual developers who handle entire projects. This has the potential to dramatically scale software engineering efforts.
- Personal task management: Agentic AI can manage calendars, schedule meetings, prioritize tasks, and summarize notes. It acts like a digital assistant with memory and decision-making ability. This helps users stay organized without constant input.
- Autonomous research agents: These agents collect, filter, and analyze information from various sources to provide insights. They can validate data, compare perspectives, and present conclusions. It’s ideal for roles in journalism, academic research, or competitive analysis.
- Customer support automation: Agentic AI can handle support tickets end-to-end, from identifying the issue to solving it or escalating when needed. It integrates with CRM systems and knowledge bases. Unlike basic chatbots, it can learn and adapt over time.
Which one should you use: Generative AI or agentic AI?
Choosing between generative AI and agentic AI depends on the nature of your tasks, business goals, and technical resources. The 2 technologies serve different purposes and understanding their strengths can help you make the right investment.
When to choose generative AI
Generative AI is ideal for organizations focused on creative output or human-AI interaction. If your team frequently needs content or assistance in areas that require ideation, writing, or designing, this is the right fit.
Consider generative AI if:
- You need to produce content at scale: Whether it’s blog articles, product descriptions, ad copy, or email drafts, generative models can significantly accelerate production.
- You want conversational assistants: Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by generative AI can respond to customer or internal queries in natural language, making support faster and more accessible.
- You aim to boost creativity: In industries like marketing, education, design, or media, Generative AI helps generate new ideas, storyboards, visuals, or learning materials.
- You’re looking for fast deployment: Many Generative AI tools are plug-and-play, allowing teams to start benefiting without deep technical integration.
- You want human-led control: Since Generative AI is prompt-based, it always acts in response to user input, giving humans full control over direction and timing.
⭐️ Unlock faster workflows with AI integration
When to choose agentic AI
Agentic AI is built for autonomous execution and goal completion. It excels in managing multi-step processes, automating workflows, and adapting to changing contexts, often without requiring constant human supervision.
Consider agentic AI if:
- You need end-to-end task automation: Agentic AI can take a high-level goal and handle every step in the process.
- You want systems that act independently: These agents can make decisions, take initiative, and follow up on tasks without waiting for constant prompts.
- Your workflows are complex and interconnected: From managing customer pipelines to executing multi-stage projects, Agentic AI can link tools, coordinate steps, and optimize execution.
- You require context-aware performance: Unlike generative models, agentic systems can remember previous actions, evaluate outcomes, and adjust their strategy over time.
- You’re seeking long-term productivity gains: While setup may take longer, Agentic AI can automate repeatable knowledge work at scale, reducing manual overhead.
Implementation considerations
Beyond use cases, there are practical factors to weigh when choosing betwee generative AI and agentic AI:
- Budget: Generative AI tools are typically more affordable and easier to implement. Agentic AI, due to its complexity, often requires custom development and system integration.
- Technical capacity: If your team lacks engineering resources, starting with Generative AI may be more realistic. Agentic systems usually need APIs, tool orchestration, and infrastructure support.
- Task nature: If your work is creative, conversational, or one-off, Generative AI is more appropriate. If your work is operational, repetitive, or goal-oriented, Agentic AI offers greater long-term efficiency.
⭐️ You might be interested in AI Outsourcing
Hybrid possibilities
In reality, many organizations benefit from hybrid systems that combine both capabilities. For example:
- An agentic AI assistant that uses a generative model to draft emails, summarize reports, or create meeting notes, then sends or organizes them automatically.
- A smart chatbot that starts as a conversational interface but escalates to an agent that can take actions like booking meetings, filing tickets, or triggering workflows.
⭐️ Explore AI chatbot for 24/7 customer support developed by Ekotek
This blending of generative AI and agentic AI allows businesses to balance control, creativity, and autonomy.
Why the shift toward agentic AI matters
The limitations of generative AI alone
Generative AI has transformed how we create content, write code, and communicate but it remains fundamentally reactive. It requires direct prompts, lacks continuity across sessions, and cannot make decisions or manage tasks independently. As business challenges grow more complex, there’s a rising need for AI that can act, adapt, and execute, not just respond.
The rise of autonomous AI systems
Agentic AI addresses these limitations by moving from passive generation to active problem-solving. With frameworks like AutoGPT, LangChain, and emerging AI agents, we now have the ability to build systems that can:
- Interpret high-level objectives and break them down into executable steps
- Chain together tools, APIs, and reasoning mechanisms to complete workflows
- Navigate ambiguity and adjust in real time, making decisions based on feedback or new information
Strategic business impacts
The adoption of agentic AI is not just a technical upgrade, it’s a strategic advantage. Companies that implement agentic systems are seeing transformative results:
- Increased productivity: AI agents handle repetitive or procedural tasks, allowing human teams to focus on strategy, creativity, and oversight.
- Operational scalability: Multiple agents can run in parallel, scaling tasks without the need to hire more staff.
- Smarter decision-making: Agentic AI can test, learn, and iterate, leading to more data-informed and adaptive operations.
A shift in human-AI collaboration
Agentic AI is not meant to replace human talent, it’s designed to amplify it. By handling structured, repeatable, or logic-driven tasks, AI agents free up human teams to focus on what they do best: creative problem-solving, relationship-building, and strategic thinking.
This shift marks the next evolution in enterprise AI, unlocking new levels of efficiency and innovation across industries.
Real-World AI in action: Ekotek case studies
Agentic AI automates BOM creation in manufacturing
Ekotek developed an AI agent to automate BOM generation for a manufacturer. The agent handles complex workflows by combining:
- Visual recognition: It scans technical drawings to identify components like outsoles, linings, and uppers.
- Language understanding: It reads catalogs, specs, and previous BOMs to extract material data.
Outcomes:
- Manual input reduced
- Faster BOM generation from design files
- Fewer errors in materials planning
💡 Want to see AI agent’s impact in detail? Read more our case study of AI-powered BOM automation
Generative AI for news summarization
A Japanese company needed a tool to help global entrepreneurs stay informed across languages. Ekotek built a solution powered by generative AI that:
- Summarizes articles using large language models (GPT-3.5)
- Translates content in over 100 languages
- Presents content in a clean, minimal interface with save-for-later features
Results:
- Faster reading time
- Improved content comprehension across languages
⭐️ Explore how we turn the client’s AI vision into reality with an AI-powered summarizing tool
Conclusion
As AI continues to evolve, understanding the distinction between generative AI and agentic AI becomes crucial. While generative AI democratized content creation and productivity, agentic AI is redefining what it means for machines to think and act. By recognizing their unique strengths and use cases, businesses can choose the right tools to solve the right problems, or better yet, combine both paradigms into a powerful AI-first strategy.
Ekotek, a trusted AI development partner with proven expertise in building both generative and agentic AI systems tailored to real business needs. From consulting to deployment, Ekotek delivers fast, scalable, and reliable AI solutions across industries, like manufacturing, banking and finance, retail and education. Our approach blends technical depth, industry insight, and agile development to help companies unlock efficiency, improve decision-making, and scale with confidence.
Ready to explore what AI can do for your business? Ekotek is here to help you build smart, future-ready solutions, the right way, from day one. Contact us today


