Blockchain in healthcare is increasingly being considered by enterprises as a solution to long-standing challenges around data fragmentation, high administrative costs, and complex regulatory compliance. As healthcare ecosystems involve multiple stakeholders, hospitals, insurers, laboratories, and suppliers, traditional centralized systems often struggle to support secure data sharing and cross-organization trust.
This article explores how blockchain in healthcare differs from conventional databases, the concrete business benefits it delivers, and the high-impact use cases where enterprises are already applying blockchain to improve efficiency, security, and collaboration across the healthcare value chain.
How Blockchain Differs from Traditional Centralized Databases
To evaluate the role of blockchain in healthcare, it is important to understand how it fundamentally differs from traditional centralized databases commonly used in enterprise systems. Centralized databases store and control data within a single organization, making them efficient for internal operations but limited when data must be shared across multiple independent parties. In healthcare, this often leads to data silos, manual reconciliation, and complex integration between hospitals, insurers, laboratories, and external partners.
Blockchain introduces a shared, distributed ledger where multiple authorized participants maintain a synchronized view of data. Instead of relying on a single central authority, blockchain ensures data integrity through cryptographic validation and consensus mechanisms. Once recorded, information cannot be altered without network agreement, creating a built-in audit trail that supports compliance and accountability. For healthcare enterprises, this means blockchain does not replace existing databases, but complements them by providing a trusted data layer for cross-organization coordination, secure data exchange, and transparent recordkeeping across the healthcare ecosystem.
| Aspect | Traditional Centralized Databases | Blockchain in Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Data ownership | Controlled by a single organization | Shared ownership among authorized stakeholders |
| Trust model | Trust placed in a central authority | Trust distributed through consensus mechanisms |
| Data integrity | Data can be modified or overwritten | Records are immutable once written |
| Auditability | Audits require manual reconciliation | Built-in, transparent audit trail |
| Data sharing | Complex integrations between parties | Native data sharing across organizations |
| Security risk | Single point of failure | Reduced risk through decentralization |
| Compliance support | Compliance handled via processes | Compliance supported by traceability and immutability |
| Scalability across partners | Limited across independent entities | Designed for multi-party ecosystems |
👉 Related insights in Blockchain for Business
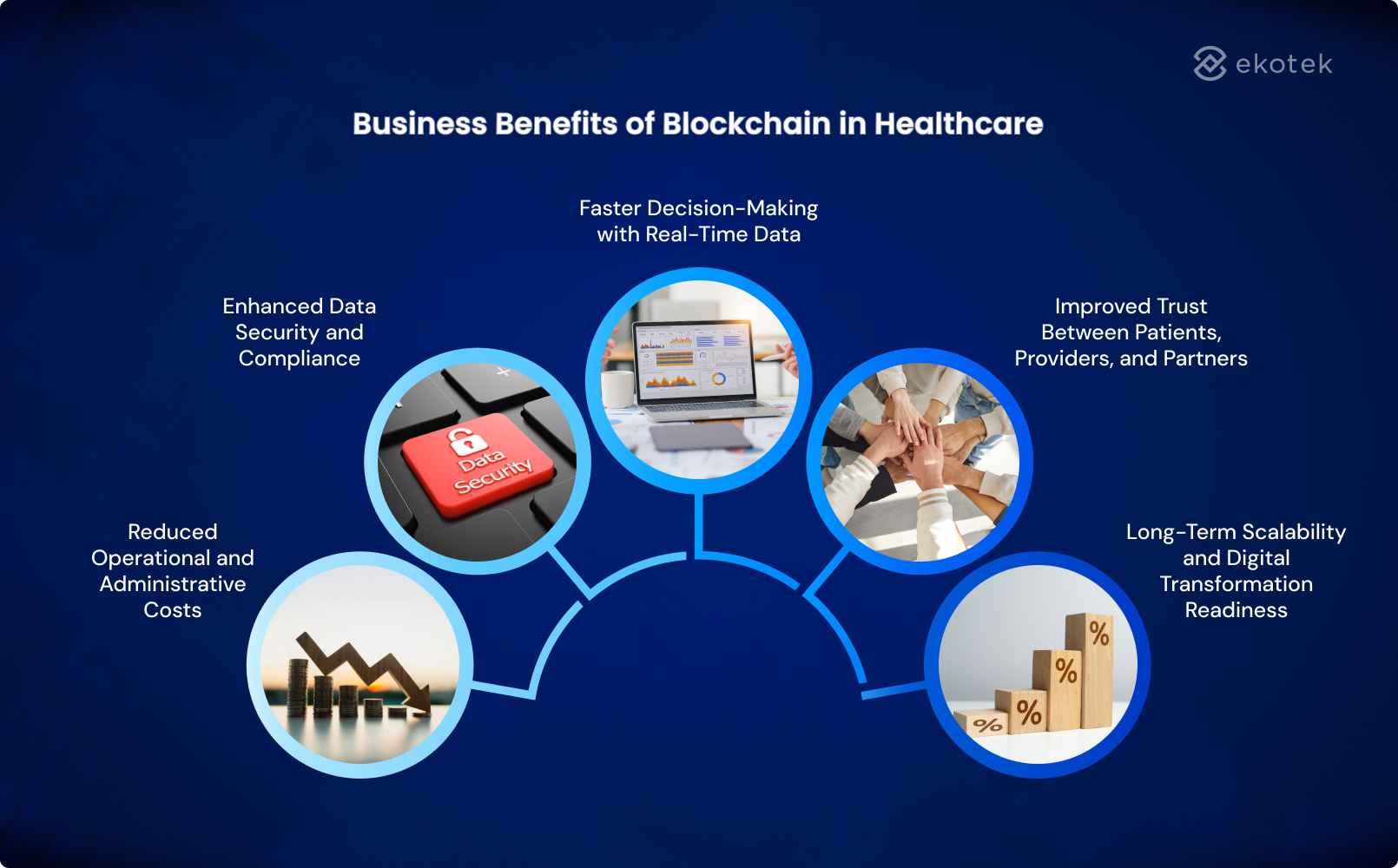
Business Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare
For healthcare enterprises, blockchain in healthcare delivers value not at the technology level, but through measurable improvements in cost efficiency, data governance, and cross-organization collaboration. When applied to the right processes, blockchain becomes a strategic enabler for both operational optimization and long-term digital transformation.
Reduced Operational and Administrative Costs
Healthcare operations often involve heavy administrative overhead due to manual verification, data reconciliation, and intermediaries between multiple parties. Blockchain reduces these costs by enabling a shared source of truth, minimizing duplicate data entry, lowering reconciliation effort, and automating processes through smart contracts.
Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Data security and regulatory compliance are critical in healthcare environments. Blockchain provides tamper-resistant recordkeeping and end-to-end traceability, supporting compliance requirements such as data integrity, access control, and audit readiness. This reduces the risk of data breaches and compliance violations while improving governance.
Faster Decision-Making with Real-Time Data
With blockchain, authorized stakeholders access synchronized, up-to-date information without relying on delayed reporting or manual data exchange. Real-time visibility into clinical, operational, or supply chain data enables faster and more informed decision-making across healthcare organizations.
Improved Trust Between Patients, Providers, and Partners
Trust is a fundamental challenge in healthcare ecosystems involving multiple independent entities. Blockchain strengthens trust by ensuring data transparency, verifiability, and controlled access, improving collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, insurers, and external partners.
Long-Term Scalability and Digital Transformation Readiness
Blockchain establishes a scalable data foundation that supports future digital initiatives such as interoperability platforms, advanced analytics, and AI-driven healthcare solutions. For enterprises, this readiness reduces future integration costs and enables sustainable digital transformation across the healthcare value chain.
High-Impact Blockchain Use Cases in Healthcare
The road from concept to real-world results can seem daunting. Consider the experience of a health system executive who, after a high-profile ransomware incident, championed blockchain for clinical data recovery, reducing impact from days to hours, and retaining stakeholder trust in the aftermath.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Blockchain is used as a shared data layer to manage access and traceability of electronic health records across healthcare providers. Instead of storing medical data directly on-chain, blockchain records permissions, data references, and access logs, enabling secure data sharing while maintaining patient control and auditability across organizations.
For example, Medicalchain uses a distributed ledger to manage patient consent and share medical records securely among clinicians, ensuring tamper-proof access logs.
Drug Supply Chain Traceability
In pharmaceutical supply chains, blockchain enables end-to-end tracking of drugs from manufacturers to distributors and healthcare providers. Each transaction or handoff is recorded on an immutable ledger, allowing stakeholders to verify product origin, monitor handling conditions, and detect counterfeit or diverted medications throughout the supply chain.
Health Insurance and Claims Processing
Blockchain supports more efficient insurance workflows by synchronizing data between healthcare providers and insurers. Claims data, policy rules, and approvals can be recorded and validated on a shared ledger, reducing manual reconciliation, preventing duplicate claims, and enabling automated processing through smart contracts.
Hashed Health pilots distributed ledger applications that synchronize claims data across payers and providers, enabling automated validation and reducing redundant reconciliation.
Clinical Trials and Research Data Integrity
Blockchain is increasingly used to ensure data integrity in clinical trials and medical research. Trial protocols, consent records, and data submissions can be timestamped and immutably recorded, helping organizations verify data authenticity, prevent tampering, and maintain transparent audit trails for regulators and research partners.
👉 From data challenges to execution with AI in Clinical Data Management
How to Get Started with Blockchain in Healthcare
You’ve evaluated the vision, now what? Business leaders and technology teams alike must take a systematic approach to realizing the full promise of blockchain, from identifying the right use case to scaling for enterprise-wide adoption.
Identify Business Pain Points
The first step is to clearly define the operational or strategic challenges that blockchain is expected to address. Common pain points include fragmented data sharing between stakeholders, high administrative overhead, lack of transparency in supply chains, or delays in insurance and compliance processes. Starting from concrete business problems helps avoid overengineering and ensures alignment with organizational priorities.
Evaluate Blockchain Feasibility
Not every problem requires blockchain. Enterprises should assess whether the use case involves multiple parties, limited trust, complex reconciliation, or strict audit requirements, conditions where blockchain delivers clear value. This evaluation should also consider regulatory constraints, data sensitivity, and integration with existing healthcare systems.
Run a Proof of Concept (PoC)
A PoC allows organizations to validate technical feasibility and business impact with limited scope and investment. At this stage, healthcare enterprises can test data flows, governance models, and interoperability with legacy systems, while gathering feedback from key stakeholders before committing to large-scale deployment.
Scale to Production
Once value is proven, the focus shifts to production readiness. This includes performance optimization, security hardening, compliance validation, and operational integration. A well-planned scaling phase ensures that blockchain solutions can support real-world healthcare workloads and evolve as part of a broader digital transformation strategy
👉 Build-ready guidance in the Blockchain Application Development Guide

Conclusion: Blockchain as a Strategic Advantage in Healthcare
As healthcare enterprises face growing pressure around cost efficiency, data security, and regulatory compliance, blockchain in healthcare is emerging as a strategic infrastructure rather than a standalone technology initiative. As outlined in this article, blockchain differs fundamentally from traditional databases by enabling trusted data sharing across multiple parties, supporting high-impact use cases such as EHR management, drug traceability, insurance claims processing, and clinical research integrity. When implemented with a clear business focus, blockchain can strengthen operational resilience while laying the foundation for long-term digital transformation.
Turning this potential into measurable outcomes requires the right execution partner. Ekotek is a leading software development firm in Vietnam, specializing in digital transformation, blockchain, and AI. Ekotek provides a full spectrum of blockchain services, including smart contracts, dApp development, blockchain integration, NFT marketplaces, Web3 gaming, and payment solutions. With an end-to-end delivery model, covering consulting, solution design, development, implementation, and ongoing maintenance, Ekotek has successfully delivered enterprise solutions across industries such as F&B, manufacturing, logistics, and fintech. In addition, Ekotek offers white-label blockchain solutions that accelerate time-to-market while remaining fully customizable to business requirements.
If your organization is exploring blockchain in healthcare and looking for a trusted partner to move from strategy to execution, connect with Ekotek to discuss how blockchain can become a sustainable competitive advantage for your business.


